Recently, Proceedings of the IEEE, the flagship journal of IEEE, released a special section “Energy Internet” jointly organized by Professor Sun Hongbin of Tsinghua University and Professor Nikos D. Hatziargyriou of the National Technical University of Athens, and published a 30-page long research paper “Energy Circuit-Based Integrated Energy Management System: Theory, Implementation, and Application” written by the Scheduling Automation Laboratory, Department of Electrical Engineering and Applied Electronics (EEA), Tsinghua University. The first author of the paper is Chen Binbin, a doctoral student from EEA, and the corresponding authors are Professor Sun Hongbin and Professor Guo Qinglai from EEA.

Cover of the Special Section
The integrated energy system, the core of the physical layer of the Energy Internet, is widely interconnected and deeply coordinated through various energy flows such as electricity, heat, cold, and gas, and has outstanding technical advantages in terms of energy supply reliability, economical efficiency, and flexibility. The Integrated Energy Management System (IEMS) is a key technology supporting the safe and economical operation of the integrated energy system. With the continuous expansion of the scale of integrated energy systems, how to realize online analysis and decision-making of has become an urgent problem to be solved for large-scale systems.
In this context, this paper firstly introduces the energy path theory for the unified modeling of multi-energy flows. By applying the deduction laws of power grid modeling from field to path, from time domain to frequency domain, from distribution to aggregation, and from component to network to the modeling of gas network and heat network, it realizes the generalization from the electricity circuit to gas circuit and heat circuit (generalized into energy flow), reveals the common law of transmission of heterogeneous energy flows such as electricity, gas, and heat, actualizes the efficient simplification of gas and heat energy flow models from partial differential equations to numerical algebraic equations, and finally establishes a network model with consistent mathematical forms and outstanding computational performance for the electricity network, gas network and heat network on different time scales.
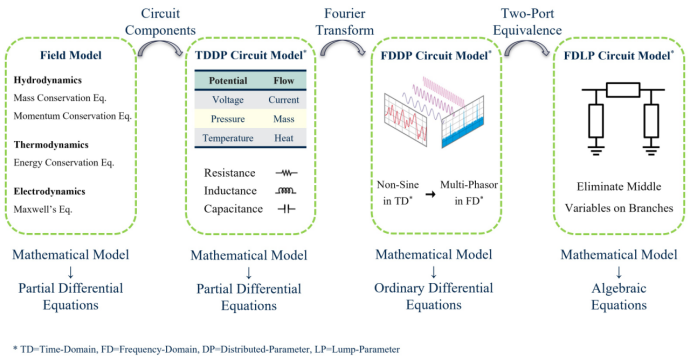
Schematic diagram for the principle of energy path theory
The paper then introduces the software architecture and functional architecture design of IEMS, further develops efficient algorithms for IEMS applications such as energy flow calculation, state estimation, optimal scheduling, safety assessment/control, etc. on the basis of the energy path method, laying a solid foundation for the development and implementation of IEMS. The numerical test results of related examples show that the integrated energy management based on the energy path method can achieve a hundred times or even a thousand times the accelerated calculation compared with the traditional method, which effectively promotes the online energy management of IEMS in large-scale integrated energy systems.

Software Architecture of IEMS
The paper also reports and summarizes the application of the above-mentioned theory and system in 12 integrated energy system demonstration projects in 10 provinces and cities in China, introduces the typical application scenarios that how IEMS supports park-level integrated energy systems, town-level integrated energy systems, provincial and municipal integrated energy systems in considerable controllability, energy saving and consumption reduction, multi-level interaction, and wind power consumption, demonstrates the broad application prospects and huge benefit space of IEMS in integrated energy systems. Finally, it summarizes the related work and looks forward to the future development of IEMS.
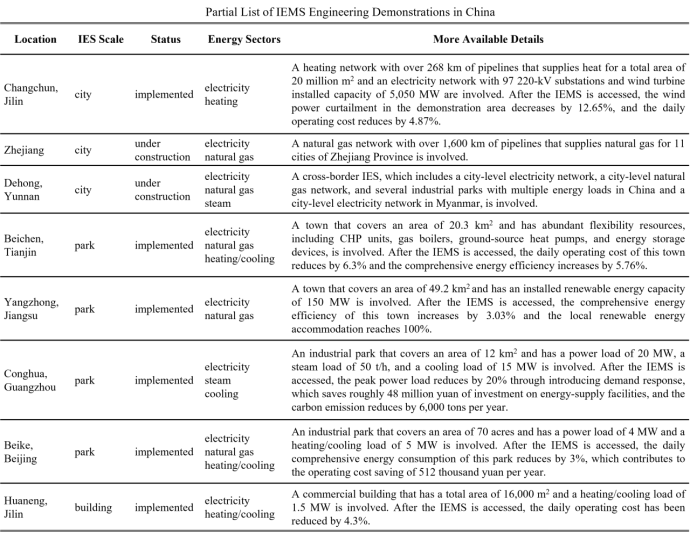
Application of IEMS in domestic demonstration projects
The Proceedings of the IEEE collects papers by invitation, this issue (volume 110, number 12), initiated by Professor Sun Hongbin, chairman of the IEEE PES Energy Internet Coordinating Committee under the theme of “Energy Internet”, sent invitation for papers to four research teams around the world, and published these papers reviewed by peers as a special section. In addition to the Scheduling Automation Laboratory of EEA, Tsinghua University, the research teams invited by this special section include the team of Professor Nikos D. Hatziargyriou from the National Technical University of Athens, the team of Professor Le Xie from Texas A&M University, and the team of Professor Jianzhong Wu from Cardiff University, UK. It involves research fields such as integrated energy management, plug-and-play technology, cyber-physical systems, and distributed ledger technology.
Citation information
Hongbin Sun and Nikos D. Hatziargyriou. “Energy Internet,” Proceedings of the IEEE, vol. 110, no. 12, pp. 1894-1896, 2022.
Binbin Chen, Qinglai Guo, Guanxiong Yin, Bin Wang, Zhaoguang Pan, Yuwei Chen, Wenchuan Wu, and Hongbin Sun. “Energy Circuit-Based Integrated Energy Management System: Theory, Implementation, and Application,” Proceedings of the IEEE, vol. 110, no. 12, pp. 1897-1926, 2022.
Team introduction
The Scheduling Automation Team of EEA, Tsinghua University, mainly engaged in the research on power grid energy management, automatic voltage control, multi-energy flow integrated energy management and artificial intelligence application, is one of the earliest units in China to start research on power grid energy management and operation control.
The team, with a history of more than 40 years, has accumulated more than 30 years of experience in the research on power grid energy management. It has developed China’s first large-scale power grid EMS application software with completely independent intellectual property rights. The EMS system, reactive voltage control system, active frequency control system and other products developed by the team have been applied to more than 100 national, provincial and prefectural power grids. The team has made world-leading achievements in both academia and industry, and won 3 prizes (1 first prize, 2 second prizes) of the National Science and Technology Award, 2 awards for Top Ten Scientific and Technological Advancement in Chinese Universities, and more than 30 provincial and ministerial science and technology awards.
In recent years, the team has taken the lead in proposing and exploring new directions of multi-energy flow energy management in China, and released the first set of multi-energy flow integrated energy management system (IEMS) at home and abroad in 2017, expanding the energy management object from “power flow” to “multi-energy flow”. In 2017, it initiated the largest international conference in the field of Energy Internet. In 2018, it was invited by the editor-in-chief to publish the first international academic paper introducing IEMS in the magazine IEEE Electrification. In 2019, it presided over the construction of the first large-scale urban energy Internet demonstration project at home and abroad. In 2020, it established and presided over the IEEE PES Energy Internet Coordinating Committee (the first PES committee established by Chinese scholars), which promoted the formation and development of emerging cross-fields of the Energy Internet.

Team photo

















 News & Events
News & Events